In the ever-evolving world of mobile phone technology, one of the most crucial elements that define our smartphone experience is the display. It’s the window to our digital world, where we interact with apps, watch videos, and navigate through our daily tasks. Mobile phone screens have come a long way from the monochrome displays of early cell phones. Among the array of display technologies available today, three popular choices stand out: OLED, AMOLED, and LCD. This comprehensive exploration delves deep into these screen technologies, unveiling their differences, advantages, and applications.
Understanding the Basics
Before we dissect the distinctions between OLED, AMOLED, and LCD screens, let’s establish a foundational understanding of these technologies.
OLED: Organic Light-Emitting Diodes
OLED, which stands for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes, is a technology that uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. Each pixel in an OLED display is a tiny, self-emissive light source, which means it can produce its own light independently. This allows for precise control of individual pixels, resulting in vibrant colors and deep blacks.
AMOLED: Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes
AMOLED, or Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes, is a variation of OLED technology. It employs an active matrix to control each pixel individually, offering improved efficiency and higher resolution. AMOLED screens are widely used in modern smartphones and high-end displays.
LCD: Liquid Crystal Display
LCD, or Liquid Crystal Display, is a well-established screen technology that has been in use for years. LCDs utilize a liquid crystal solution placed between two layers of glass. These crystals are manipulated to control the passage of light through each pixel, which is typically illuminated by a separate backlight.
Now that we have a basic understanding of these technologies, let’s delve into the specifics.
Display Quality
OLED: The King of Contrast
One of the most significant advantages of OLED displays is their ability to produce perfect blacks. In an OLED screen, each pixel can be turned on or off independently, meaning black areas of the screen are truly black, with no light bleed. This feature contributes to exceptional contrast ratios and makes OLED displays ideal for watching movies or viewing content with deep blacks and vibrant colors.
Advantages of OLED Display Quality:
- Perfect blacks and infinite contrast ratios.
- Vibrant colors and wide color gamut.
- Fast response times for smooth animations.
Disadvantages of OLED Display Quality:
- Susceptibility to burn-in with static images.
- Variable color accuracy over time.
AMOLED: Excellence in Mobile Displays
AMOLED screens inherit the advantages of OLED technology. They also offer deep blacks and vibrant colors, making them an excellent choice for mobile devices. The active matrix control in AMOLED screens further enhances the overall display quality, resulting in sharper images and better power efficiency.
Advantages of AMOLED Display Quality:
- Excellent contrast and vibrant colors.
- Active matrix control for improved sharpness.
- Power-efficient, especially with dark-themed interfaces.
Disadvantages of AMOLED Display Quality:
- Vulnerable to burn-in.
- Slight color degradation over time.
LCD: Reliable and Proven
LCDs have long been a reliable choice for screen technology. They offer good color accuracy and are less susceptible to burn-in compared to OLED screens. However, LCDs struggle to achieve the same level of contrast and black levels as OLED and AMOLED displays due to the need for a backlight.
Advantages of LCD Display Quality:
- Good color accuracy and longevity.
- Reduced risk of burn-in.
- Bright and visible in direct sunlight.
Disadvantages of LCD Display Quality:
- Limited contrast and black levels.
- Backlight bleeding in some cases.
Power Efficiency
OLED: Pixel-Level Control
OLED displays have a significant advantage in power efficiency because of their pixel-level control. When a pixel is turned off, it consumes no power, which is particularly beneficial when displaying dark content or using dark-themed interfaces. This feature contributes to better battery life in situations where the majority of the screen is displaying black or dark colors.
Advantages of OLED Power Efficiency:
- Low power consumption for dark content.
- Efficient for devices with OLED-specific power-saving features.
Disadvantages of OLED Power Efficiency:
- Higher power usage for bright and white content.
- Potential for accelerated burn-in with constant display of static elements.
AMOLED: Enhanced Efficiency
AMOLED screens also benefit from pixel-level control, leading to efficient power usage, especially in dark-themed apps or content. Manufacturers often implement power-saving features specific to AMOLED displays to optimize battery life further.
Advantages of AMOLED Power Efficiency:
- Efficient power consumption with dark content.
- Enhanced battery life through AMOLED-specific optimizations.
Disadvantages of AMOLED Power Efficiency:
- Higher power usage for bright content.
- Potential for burn-in with static elements.
LCD: Backlight Dependency
LCDs rely on a backlight to illuminate the entire screen, which means they consume a relatively constant amount of power regardless of the content displayed. While LCDs have become more power-efficient over the years, they still struggle to compete with OLED and AMOLED displays in terms of power efficiency, especially when rendering dark or predominantly black content.
Advantages of LCD Power Efficiency:
- Relatively consistent power consumption.
- Improved power-saving technologies in modern LCD displays.
Disadvantages of LCD Power Efficiency:
- Inefficient for dark content.
- Inferior power efficiency in comparison to OLED technologies.
Durability
OLED: Sensitive to Stress
OLED displays are more susceptible to physical damage than LCDs due to their organic nature. When subjected to pressure or impact, OLED pixels can become damaged, resulting in permanent white or colored spots on the screen. This susceptibility to stress can make OLED screens more delicate and prone to damage.
Advantages of OLED Durability:
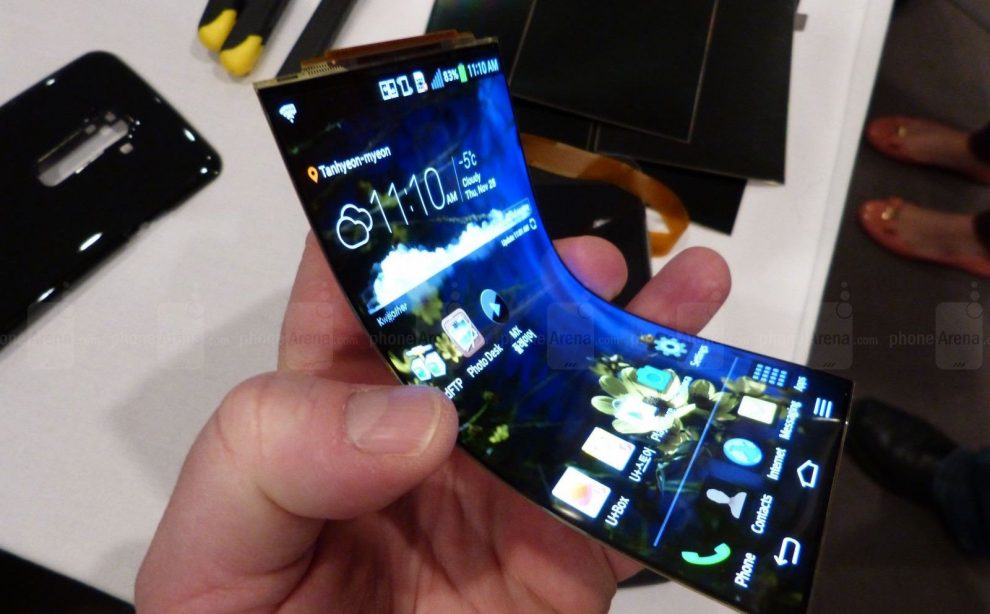
- Lightweight and flexible, suitable for curved and foldable displays.
- High flexibility for innovative form factors.
Disadvantages of OLED Durability:
- Sensitive to stress and physical damage.
- Potential for permanent screen burn-in.
AMOLED: Balanced Durability
AMOLED displays share the same vulnerability to physical damage as OLED screens. However, manufacturers often reinforce AMOLED displays with protective layers, making them slightly more robust and resistant to stress. They are still more delicate than LCD screens, but these protective measures improve overall durability.
Advantages of AMOLED Durability:
- Slightly more robust than standard OLED displays.
- Support for flexible and foldable displays.
Disadvantages of AMOLED Durability:
- Vulnerable to physical damage.
- Possibility of screen burn-in.
LCD: Sturdy and Resilient
LCD screens, being made of rigid glass, are generally more durable and resistant to physical damage compared to OLED and AMOLED displays. The risk of screen damage due to stress or pressure is lower, making LCDs a practical choice for users who prioritize durability.
Advantages of LCD Durability:
- Sturdy and less susceptible to physical damage.
- Reduced risk of screen burn-in.
Disadvantages of LCD Durability:
- Heavier and less suitable for innovative form factors.
Viewing
Angles and Visibility
OLED: Wide Viewing Angles
OLED displays offer wide viewing angles, meaning you can view the screen from various positions without significant loss of image quality or color accuracy. This feature is particularly advantageous for smartphones and TVs, where multiple viewers may be watching from different angles.
Advantages of OLED Viewing Angles:
- Wide and consistent viewing angles.
- Minimal color shift at extreme angles.
Disadvantages of OLED Viewing Angles:
- Potential for brightness and color variations with age.
- Slight distortion in some flexible OLED displays.
AMOLED: Similar to OLED
AMOLED displays share the same wide viewing angles as OLED screens, thanks to their similar underlying technology. Users can enjoy consistent image quality from various angles, making AMOLED screens ideal for smartphones and other portable devices.
Advantages of AMOLED Viewing Angles:
- Wide and consistent viewing angles.
- Suitable for devices with multiple users.
Disadvantages of AMOLED Viewing Angles:
- Potential for brightness and color variations with age.
- Slight distortion in flexible AMOLED displays.
LCD: Respectable Viewing Angles
LCD screens also offer good viewing angles, although they may not match the wide angles provided by OLED and AMOLED displays. Users can still enjoy decent image quality when viewing an LCD screen from different positions, but there may be some minor shifts in brightness and color accuracy.
Advantages of LCD Viewing Angles:
- Respectable viewing angles for most use cases.
- Suitable for single-user devices.
Disadvantages of LCD Viewing Angles:
- Limited compared to OLED and AMOLED.
- Slight color and brightness shifts at extreme angles.
Outdoor Visibility
OLED: Mixed Outdoor Performance
OLED screens often offer excellent visibility outdoors due to their high brightness levels. However, the performance of OLED displays can vary between different devices. Some OLED screens may struggle to compete with direct sunlight, while others excel in this regard.
Advantages of OLED Outdoor Visibility:
- High brightness levels for improved outdoor visibility.
- Varies by device; some OLED screens perform well outdoors.
Disadvantages of OLED Outdoor Visibility:
- Inconsistent outdoor performance across devices.
- Potential for screen reflections in direct sunlight.
AMOLED: Varies by Device
AMOLED displays exhibit similar outdoor visibility characteristics to OLED screens, with some variability between devices. The quality of outdoor visibility largely depends on the specific AMOLED panel and the device’s design. Some AMOLED screens perform exceptionally well outdoors, while others may struggle.
Advantages of AMOLED Outdoor Visibility:
- High brightness levels for improved outdoor visibility.
- Varies by device; some AMOLED screens perform well outdoors.
Disadvantages of AMOLED Outdoor Visibility:
- Inconsistent outdoor performance across devices.
- Potential for screen reflections in direct sunlight.
LCD: Typically Good Outdoor Visibility
LCD screens are known for their respectable outdoor visibility. Most LCD-equipped devices offer good performance in direct sunlight, thanks to their high brightness levels. This makes LCD screens a reliable choice for users who frequently use their devices outdoors.
Advantages of LCD Outdoor Visibility:
- Consistently good outdoor visibility.
- Reliable performance in direct sunlight.
Disadvantages of LCD Outdoor Visibility:
- Slight reflections in bright sunlight may be present.
Price and Availability
OLED: Premium Pricing
OLED displays are often associated with premium smartphones and high-end TVs. Due to their manufacturing costs and the quality they offer, devices with OLED screens tend to be more expensive than those with LCD screens. However, OLED technology has become more prevalent in recent years, making it increasingly accessible.
Advantages of OLED Price and Availability:
- Premium display quality.
- Widely available in high-end devices.
Disadvantages of OLED Price and Availability:
- Higher costs for devices with OLED screens.
- Limited availability in budget-friendly options.
AMOLED: Varied Pricing
AMOLED screens come in a variety of devices, ranging from mid-range smartphones to high-end flagship models. This variation in pricing and availability makes AMOLED technology accessible to a broader range of consumers. Users can choose from a selection of devices that match their budget.
Advantages of AMOLED Price and Availability:
- Available in a wide range of devices.
- Options for both mid-range and high-end consumers.
Disadvantages of AMOLED Price and Availability:
- Premium AMOLED devices still come at a cost.
- Limited availability in ultra-budget devices.
LCD: Budget-Friendly Options
LCD screens are commonly found in budget-friendly smartphones and devices. They are a cost-effective choice for manufacturers, which often results in more affordable options for consumers. If you’re looking for a capable device without breaking the bank, LCD-equipped devices are readily available.
Advantages of LCD Price and Availability:
- Budget-friendly display technology.
- Widespread availability in various devices.
Disadvantages of LCD Price and Availability:
- Lower quality compared to OLED and AMOLED.
- Limited availability in high-end flagship models.
Burn-In
OLED: Susceptible to Burn-In
One notable drawback of OLED screens is their susceptibility to burn-in, a phenomenon where static elements displayed on the screen for extended periods can leave a permanent imprint. This issue is especially prevalent in OLED screens used in televisions and smartphones with static elements, such as navigation bars and logos.
Advantages of OLED in Terms of Burn-In:
- None.
Disadvantages of OLED in Terms of Burn-In:
- Vulnerable to burn-in, especially in devices with static elements.
- Risk of uneven wear with varied usage patterns.
AMOLED: Share the Same Risk
AMOLED displays share the same risk of burn-in as OLED screens. While manufacturers implement measures to mitigate this issue, it remains a concern for devices with static UI elements or constant display of the same content.
Advantages of AMOLED in Terms of Burn-In:
- None.
Disadvantages of AMOLED in Terms of Burn-In:
- Vulnerable to burn-in, especially in devices with static elements.
- Risk of uneven wear with varied usage patterns.
LCD: Burn-In Immune
LCD screens do not suffer from burn-in issues like OLED and AMOLED displays. Since LCDs rely on a backlight to illuminate the screen and do not have self-emissive pixels, the risk of permanent burn-in is virtually non-existent.
Advantages of LCD in Terms of Burn-In:
- Immune to burn-in issues.
- Suitable for devices with static elements.
Disadvantages of LCD in Terms of Burn-In:
- None.
Color Accuracy and Calibration
OLED: Excellent Color Accuracy
OLED screens generally provide excellent color accuracy, offering vibrant and true-to-life colors. However, the accuracy of OLED displays may drift slightly over time due to the organic nature of the materials used in their construction.
Advantages of OLED Color Accuracy:
- Excellent color accuracy, especially when new.
- Vibrant and true-to-life colors.
Disadvantages of OLED Color Accuracy:
- Slight color accuracy variations over time.
- Potential for color shift with age.
AMOLED: Similar to OLED
AMOLED displays share the same color accuracy characteristics as OLED screens. When new, they deliver excellent color reproduction, but slight variations may occur over time.
Advantages of AMOLED Color Accuracy:
- Excellent color accuracy, especially when new.
- Vibrant and true-to-life colors.
Disadvantages of AMOLED Color Accuracy:
- Slight color accuracy variations over time.
- Potential for color shift with age.
LCD: Good Color Accuracy
LCD screens also offer good color accuracy, though they may not match the exceptional accuracy of OLED and AMOLED displays. Users can expect accurate and natural color representation on most LCD-equipped devices, making them suitable for various content consumption.
Advantages of LCD Color Accuracy:
- Good color accuracy for most use cases.
- Suitable for general content consumption.
Disadvantages of LCD Color Accuracy:
- Not as exceptional as OLED and AMOLED displays.
- Slight color variations may be present.
Power Efficiency
OLED: Power-Efficient in Certain Scenarios
OLED screens can be power-efficient in specific usage scenarios. Since each pixel is individually lit and can be turned on or off independently, OLED technology is well-suited for displaying content with deep blacks, as black pixels are essentially turned off, consuming no power. However, in scenarios with predominantly bright content, OLED displays may consume more power than LCD screens.
Advantages of OLED Power Efficiency:
- Power-efficient when displaying content with deep blacks.
- Efficient in scenarios with mixed content.
Disadvantages of OLED Power Efficiency:
- Consumes more power with predominantly bright content.
- OLED technology varies in power efficiency.
AMOLED: Power-Efficient in Certain Scenarios
AMOLED displays exhibit power efficiency characteristics similar to OLED screens. They excel in scenarios with predominantly dark or mixed content, as black pixels are turned off, conserving power. However, when displaying predominantly bright content, power consumption may increase compared to LCD screens.
Advantages of AMOLED Power Efficiency:
- Power-efficient when displaying content with deep blacks.
- Efficient in scenarios with mixed content.
Disadvantages of AMOLED Power Efficiency:
- Consumes more power with predominantly bright content.
- AMOLED technology varies in power efficiency.
LCD: Consistent Power Consumption
LCD screens offer consistent power consumption across various usage scenarios. While they may not provide the same power-saving benefits as OLED and AMOLED displays when displaying deep blacks, they also do not consume significantly more power when displaying bright content.
Advantages of LCD Power Efficiency:
- Consistent power consumption in all scenarios.
- Suitable for a wide range of usage patterns.
Disadvantages of LCD Power Efficiency:
- May not offer the same power savings as OLED and AMOLED with dark content.
Lifespan
OLED: Limited Lifespan
OLED screens have a limited lifespan compared to LCD displays. Over time, the organic materials in OLED panels can degrade, leading to issues such as burn-in and color accuracy drift. The lifespan of OLED screens can vary depending on usage and the quality of the panel.
Advantages of OLED Lifespan:
- None.
Disadvantages of OLED Lifespan:
- Limited lifespan with potential for burn-in and color accuracy issues.
- Lifespan varies by device quality and usage patterns.
AMOLED: Similar Lifespan to OLED
AMOLED displays share a similar limited lifespan to OLED screens due to their common underlying technology. Like OLED, AMOLED panels can experience issues such as burn-in and color accuracy drift over time.
Advantages of AMOLED Lifespan:
- None.
Disadvantages of AMOLED Lifespan:
- Limited lifespan with potential for burn-in and color accuracy issues.
- Lifespan varies by device quality and usage patterns.
LCD: Longer Lifespan
LCD screens generally have a longer lifespan compared to OLED and AMOLED displays. The absence of organic materials that degrade over time contributes to their durability. LCD-equipped devices can maintain their image quality for a more extended period, making them a reliable choice for long-term use.
Advantages of LCD Lifespan:
- Longer lifespan with less risk of burn-in and color accuracy issues.
- Durable and suitable for long-term use.
Disadvantages of LCD Lifespan:
- None.
Screen Technology Comparison Summary
To summarize the comparison of OLED, AMOLED, and LCD screens:
- **Viewing Angles:**Â OLED and AMOLED offer wide viewing angles, while LCD provides respectable angles.
- **Outdoor Visibility:**Â OLED, AMOLED, and LCD screens vary in outdoor performance.
- **Price and Availability:**Â OLED screens are associated with premium devices, AMOLED offers varied pricing, and LCD is budget-friendly.
- **Burn-In:**Â OLED and AMOLED screens are susceptible to burn-in, while LCD screens are immune.
- **Color Accuracy and Calibration:**Â OLED and AMOLED provide excellent color accuracy, with LCD offering good accuracy.
- **Power Efficiency:**Â OLED and AMOLED are power-efficient in certain scenarios, while LCD offers consistent power consumption.
- **Lifespan:**Â OLED and AMOLED have a limited lifespan, while LCD screens have a longer lifespan.
Your choice between OLED, AMOLED, and LCD screens should depend on your specific needs, budget, and usage patterns. Each technology has its strengths and weaknesses, so consider the factors that matter most to you when selecting a device.













Add Comment